Introduction to Blockchain Technology
What is Blockchain in Simple Terms?
Let’s break it down—blockchain might sound like a term from a sci-fi novel, but it’s a revolutionary piece of technology that’s already reshaping the digital world. Imagine a digital ledger, like a record book, but instead of being stored in one place like a traditional database, it’s duplicated and distributed across a network of computers. Each entry in this ledger is called a “block,” and these blocks are linked together chronologically to form a “chain”—hence the name blockchain.
Here’s the cool part: once a piece of information goes into this chain, it’s almost impossible to alter it without changing every single block that came after it—which would require the consensus of every participant in the network. That’s what makes blockchain incredibly secure and transparent.
This technology was initially created to support cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but it has grown far beyond that. From securing medical records to transforming how votes are counted, blockchain offers possibilities that were once thought impossible. And the best part? You don’t need to be a tech wizard to grasp the basics. This article will guide you through blockchain step by step—no jargon, no assumptions.
Why Is Blockchain Important in Today’s World?
We’re living in a time where digital trust is everything. With countless data breaches, fraud scandals, and privacy concerns hitting headlines regularly, the way we store and share information needs a serious upgrade. That’s where blockchain steps in. It offers a system where transactions and records are not just stored but verified and protected in a decentralized manner.
For industries that rely heavily on trust—think banking, healthcare, logistics, or even voting—blockchain is a game-changer. It reduces the need for middlemen, cuts down fraud, and boosts efficiency. For example, in the finance world, blockchain enables quicker, cheaper cross-border payments without traditional banking delays.
Even beyond business, blockchain empowers individuals. You own your data, your assets, and your privacy in a way traditional systems just don’t allow. It’s like giving the internet a much-needed ethical upgrade.
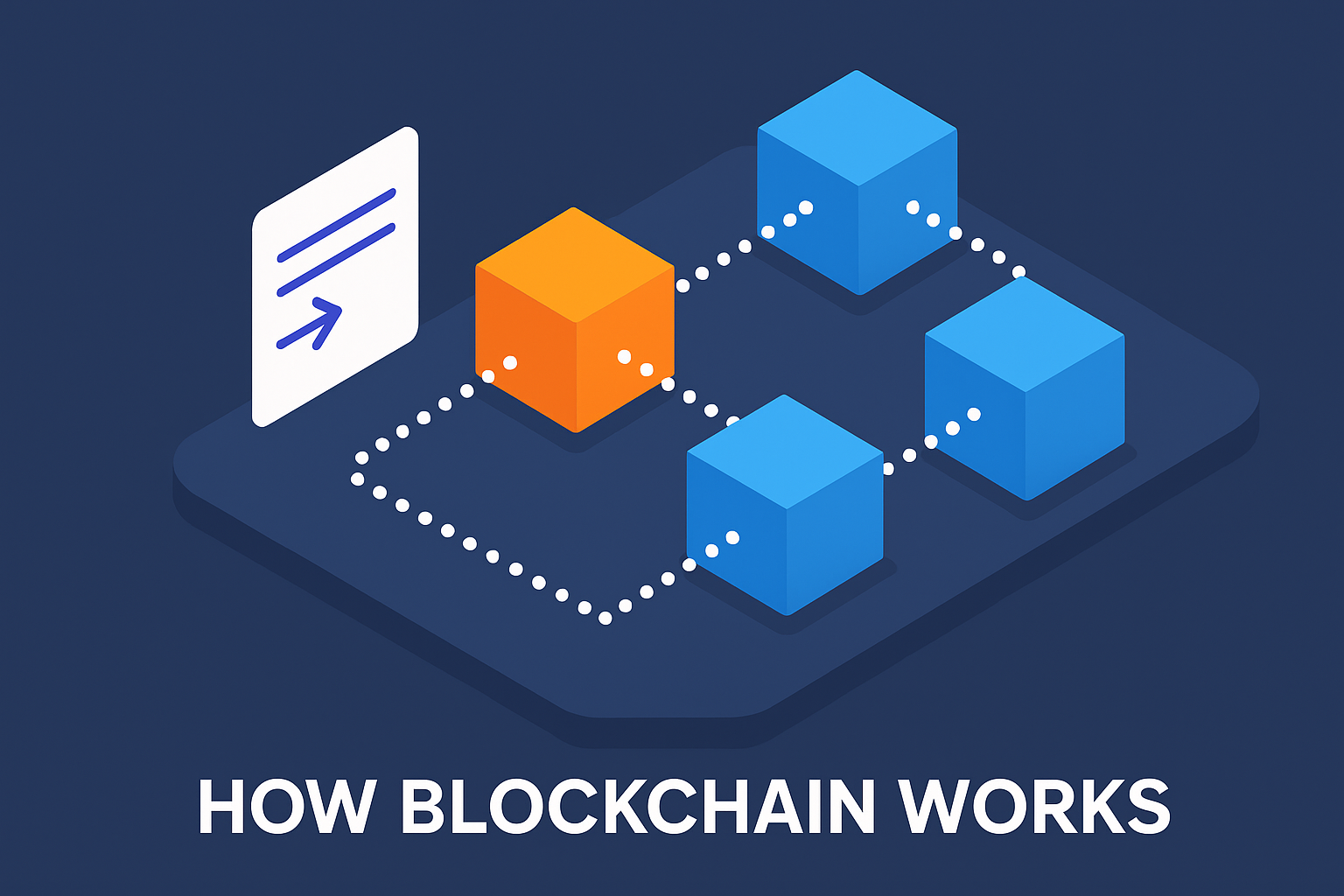
The Core Concept: Blocks and Chains
Understanding Blocks: The Basic Units
Think of a block as a digital container that holds a group of transactions or data entries. Each block has three main components: data, a unique hash (a kind of digital fingerprint), and the hash of the previous block. That hash connects each block to the one before it, creating a secure and traceable link between them.
The data inside the block depends on the type of blockchain. In Bitcoin, for example, a block might contain details like the sender, receiver, and amount of cryptocurrency exchanged. Other blockchains might store contract terms, medical records, or supply chain info.
But it’s the hash that makes it special. If someone tries to alter the contents of a block, the hash changes. This sets off a chain reaction that breaks the connection with every subsequent block—making tampering immediately obvious and practically impossible.
Linking the Chain: How Blocks Form a Network
Each block isn’t just sitting alone. Once verified, it connects securely to the previous block, forming a continuous chain of blocks—hence the name blockchain. This chronological structure makes it easy to trace any piece of information back to its origin.
The magic lies in its distributed nature. Instead of one central computer or server controlling the chain, it’s managed by a network of computers (called nodes), all of which hold a copy of the blockchain. When a new block is added, every node updates their copy to reflect the change. If someone tries to cheat the system by adding a false block, it’s rejected by the other nodes because it doesn’t match their records.
This decentralized, transparent structure makes blockchain one of the most secure and tamper-proof technologies available today. It’s not just trustless—it creates trust by design.
How Blockchain Works Step by Step
Step 1 – A Transaction is Requested
Let’s start with the beginning of any blockchain process—a transaction. This could be anything from sending cryptocurrency to signing a digital contract. The transaction contains specific details: who’s involved, what’s being transferred, and when it’s happening. Once initiated, this transaction is not immediately processed like in traditional systems. Instead, it gets packaged and sent to a decentralized network of computers—known as nodes.
Now, here’s where things get interesting. Unlike banks or centralized platforms that process transactions behind closed doors, blockchain broadcasts your request across its network. Every node receives the same transaction data, and they all get to work verifying it. That’s right—everyone gets a say. This is the cornerstone of decentralization.
What makes this powerful is that no single party can fake a transaction. If someone tries to spend the same digital coin twice, or if a hacker attempts to alter the transaction details, the other nodes will detect the discrepancy and reject it. It’s like having hundreds or thousands of vigilant digital referees watching every move.
Step 2 – The Transaction is Broadcast to the Network
Once a transaction is created, it’s broadcast to a network of peer-to-peer nodes. Each node runs a copy of the blockchain software and independently checks the transaction’s legitimacy. This broadcasting is essential to maintaining transparency and eliminating centralized control.
Imagine a digital town hall, where instead of whispering to a single bank, your transaction is announced publicly. Everyone hears it, everyone checks it, and everyone agrees on whether it should be accepted.
This process ensures that there’s no single point of failure. Even if one node goes down or acts maliciously, the rest of the network continues functioning smoothly. In fact, for a transaction to move forward, a consensus mechanism kicks in. Depending on the blockchain type, this could be Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, or another method used to validate and agree on transaction legitimacy.
So, the network is essentially crowd-verifying every transaction. That’s how you know it’s solid, secure, and tamper-resistant.
Types of Blockchains Explained
Public Blockchain
A public blockchain is open to anyone. Anyone can join the network, read the data, create transactions, and participate in the consensus process. It’s the most decentralized form and the foundation for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
The key advantage here? Transparency. Everyone can see everything. While your personal identity remains hidden behind cryptographic addresses, all activity is visible. That’s a huge deal for accountability. No one can tamper with the system without everyone knowing.
Because it’s so open, public blockchains are also extremely secure. They operate on massive networks with thousands of nodes, making it nearly impossible for hackers to compromise the system. But this openness comes at a cost—mainly slower transaction speeds and higher energy consumption.
Still, for applications like global currencies, decentralized apps, and smart contracts, public blockchains are the gold standard.
Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are more controlled. Think of them like a private club—only select members can join, view, or participate in the blockchain. This setup is often used by companies and organizations that need blockchain’s benefits without exposing sensitive data to the public.
Private blockchains offer faster performance, higher scalability, and more customization options. However, they sacrifice some of the decentralization and transparency found in public chains.
They’re great for internal company use, supply chain management, or enterprise data tracking, where speed and privacy are more important than public accessibility.
Consortium Blockchain
This type sits between public and private blockchains. A consortium blockchain is controlled by a group rather than a single organization. It offers partial decentralization while maintaining efficiency and speed.
Picture a group of banks using a shared blockchain to verify interbank transactions. Each bank has a node, and they collectively validate data. It’s faster than public blockchains and more trustworthy than a private one.
Consortium chains are gaining popularity in sectors like finance, insurance, and supply chain logistics—where collaboration is essential but full transparency isn’t.
Hybrid Blockchain
As the name implies, hybrid blockchains blend features of both public and private networks. They allow organizations to control who can access specific data while also using public blockchain features for greater transparency where needed.
Think of a healthcare system where patient data is privately stored, but medical procedures and treatments are logged publicly to prevent malpractice. Hybrid models give businesses the best of both worlds: transparency where it’s needed, and privacy where it matters.
Key Features That Make Blockchain Revolutionary
Decentralization
Decentralization is the heartbeat of blockchain. In a decentralized system, no single entity has total control. Instead, authority and decision-making are distributed across a network. This eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks, governments, or tech giants.
Why does this matter? Because decentralization empowers users. It returns control over data and digital assets to individuals. Whether it’s your money, your health records, or your vote, decentralization ensures no central authority can manipulate or censor your actions.
Moreover, it increases system resilience. There’s no central server to attack, no single failure point to exploit. The entire network would have to be compromised—which is nearly impossible on large-scale blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Decentralization is what makes blockchain fair, open, and nearly immune to corruption.
Immutability
Immutability means once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted. This is achieved through cryptographic hashing and consensus algorithms. Each block has a hash and a reference to the previous block’s hash, creating a chain that’s extremely hard to alter.
Why is this a big deal? Because it creates a permanent, tamper-proof record. In finance, this prevents fraud. In healthcare, it ensures accurate patient histories. In supply chains, it proves product authenticity.
It also boosts accountability. If someone tries to alter the blockchain, every node in the network would notice and reject the change. This means records are more trustworthy than ever before—an essential feature in our increasingly digital world.
Transparency and Trust
Blockchain is transparent by design. Anyone can inspect the data on a public blockchain. Even though personal details remain encrypted, all transactions are visible and verifiable by every participant in the network.
This transparency builds trust without the need for intermediaries. You don’t have to “trust” the other party—you trust the system.
Imagine donating to a charity and being able to trace exactly how your money is spent. Or voting in an election and instantly confirming your vote was counted. That’s the kind of trust blockchain delivers.
In short, transparency and immutability create a system where truth becomes the default—and manipulation gets sidelined.
Blockchain vs Traditional Databases
Centralized vs Decentralized Systems
Traditional databases are centralized. They’re controlled by a single entity—like a company or a bank—who decides who gets access, how data is managed, and what happens when something goes wrong.
Blockchain flips that on its head. It operates on a peer-to-peer network where data is shared, verified, and managed collectively. There’s no central boss, just a transparent system where everyone participates equally.
This reduces vulnerability. If a centralized database is hacked, the attacker can access or even delete sensitive information. But on a decentralized blockchain, that’s nearly impossible. It would require hacking thousands of computers simultaneously—an almost unachievable feat.
This structure also enhances fairness. No single party can manipulate records to their advantage, because any attempt would be rejected by the rest of the network.
Data Integrity and Tamper Resistance
In traditional systems, data can be altered or deleted by anyone with administrative access. This opens the door for fraud, data loss, or manipulation.
Blockchain ensures data integrity through cryptographic validation. Each block’s hash is calculated based on its contents and the hash of the block before it. If even one piece of data changes, the entire chain becomes invalid.
This makes tampering nearly impossible. Not only would a hacker need to alter one block, but they’d also have to redo the work for every block after it—on every node in the network—before anyone notices. That’s a level of security traditional databases simply can’t match.
Blockchain offers a new gold standard for data security, reliability, and accountability in a digital age increasingly plagued by cyber threats.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Financial Services and Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain is most famously known for powering cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These digital currencies operate without a central bank, allowing people to transfer value directly to each other worldwide, 24/7.
But it doesn’t stop there. Banks and financial institutions are adopting blockchain for fast, low-cost transactions, fraud reduction, and better compliance. Blockchain cuts out intermediaries, making transactions faster and cheaper. It also creates an unchangeable audit trail for every cent moved—a dream for regulators and auditors.
From international remittances to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms that offer loans without banks, blockchain is revolutionizing how we think about money.
Supply Chain Management
In global supply chains, transparency and traceability are everything. Blockchain provides a real-time ledger that tracks goods from origin to delivery. This helps verify authenticity, reduce fraud, and identify bottlenecks.
For example, luxury brands use blockchain to prove their products aren’t counterfeits. Food companies use it to trace contaminated items to their source instantly. The result? Fewer recalls, less waste, and more trust.
It turns the entire supply chain into a transparent map that anyone can verify—a massive leap in efficiency and integrity.
Healthcare and Records Security
In healthcare, data accuracy and privacy are critical. Blockchain provides a secure, tamper-proof system for storing medical records. Patients can control who accesses their data and ensure it’s accurate and up-to-date.
Hospitals can quickly share patient histories, doctors can access verified information, and researchers can use anonymized data without privacy risks. It’s a win-win for patients, providers, and policymakers.
Voting Systems
Imagine voting in an election from your phone, with complete confidence that your vote will be counted and can’t be changed. That’s the promise of blockchain-based voting systems.
They ensure transparency, prevent fraud, and boost trust in democratic processes. While still in early stages, pilots in places like Estonia and West Virginia have shown how blockchain can modernize voting and reduce interference.
Common Myths About Blockchain
Blockchain is Only for Bitcoin
One of the biggest misconceptions about blockchain is that it’s only useful for Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. While it’s true that Bitcoin was the first major application of blockchain technology, the possibilities go far beyond digital money.
Today, blockchain is being used in everything from supply chains to digital identity, real estate, entertainment, and even art through NFTs (non-fungible tokens). The technology’s ability to create secure, transparent, and tamper-proof records means it can be applied to virtually any system where trust and verification are needed.
It’s like saying the internet is only for email. Sure, that’s where it started, but look at it now. Blockchain is following the same evolutionary path—starting with currency, but expanding into an entire ecosystem of decentralized solutions.
Blockchain is Totally Anonymous
Blockchain is actually pseudonymous—not anonymous. Each user is represented by a string of characters (a public address), but that doesn’t mean their actions are hidden. In fact, every transaction is publicly visible on the blockchain.
With some effort and the right tools, those addresses can sometimes be traced back to real identities, especially on public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum. For true anonymity, specialized privacy coins (like Monero or Zcash) are used.
So, while you’re not using your real name on the blockchain, your digital footprint is still very visible. It’s a bit like being in a room full of people wearing masks—you can’t see their faces, but you can watch everything they do.
Blockchain is Too Complicated for Regular People
Yes, the tech behind blockchain can get deeply complex—cryptographic hashing, consensus algorithms, Merkle trees. But here’s the good news: You don’t need to understand all that to use blockchain.
Just like you don’t need to know how TCP/IP works to send an email or how the banking backend functions to use an ATM, blockchain can be simplified through user-friendly interfaces. Already, wallets, exchanges, and apps have made it accessible to non-techies.
The key is education and good design. As blockchain technology matures, it’s becoming more intuitive and easier to use, just like the internet did in the 1990s.
Blockchain and the Future of Technology
Web 3.0 and Decentralized Internet
Web 3.0 is the next generation of the internet—an internet powered by blockchain, where users control their own data, identities, and digital assets. Unlike Web 2.0, dominated by centralized platforms like Google, Facebook, and Amazon, Web 3.0 is about decentralization and user empowerment.
With blockchain, data is no longer stored in a single place. It’s distributed across a network, making censorship and data manipulation much harder. Imagine owning your social media posts, your search history, and your personal information—not renting it from tech giants.
Web 3.0 is already taking shape through decentralized apps (dApps), decentralized storage (like IPFS), and blockchain-based identities. It’s a massive shift in how we interact online and could redefine digital freedom as we know it.
Smart Contracts and Automation
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements written in code. Once conditions are met, the contract executes automatically—no lawyers, no middlemen, no delays.
For instance, a smart contract in real estate could release a property title as soon as payment is made. In logistics, it could trigger payments upon successful delivery. These automated contracts reduce errors, costs, and the need for trust between parties.
Smart contracts are powering everything from DeFi apps to NFT marketplaces, and they’re only getting smarter and more integrated.
The Role of Blockchain in Emerging Tech
Blockchain isn’t just a standalone innovation—it’s a foundational layer for other emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and virtual reality (VR).
Imagine AI algorithms that are transparent and verifiable, or IoT devices that log their activity securely on a blockchain. Even in VR and the metaverse, blockchain ensures ownership of digital assets, secure identity, and real-world value transfer.
Together, these technologies form a digital renaissance—a new era where trust is built into the system, not bolted on as an afterthought.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain
Scalability Issues
While blockchain offers unmatched security and transparency, scalability remains a major hurdle. Networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum can only process a limited number of transactions per second, far less than traditional systems like Visa or Mastercard.
This bottleneck leads to slower transaction times and higher fees during periods of heavy usage. Solutions like Layer 2 protocols (e.g., Lightning Network), sharding, and more efficient consensus mechanisms (like Proof of Stake) are being developed to tackle this issue.
Still, achieving scalability without compromising decentralization and security—the so-called blockchain trilemma—is a balancing act that’s still being perfected.
Regulatory and Legal Concerns
Blockchain operates across borders, which creates legal grey areas. Who governs decentralized systems? How do you handle disputes in smart contracts? What happens when someone loses access to their digital wallet?
Governments around the world are grappling with how to regulate blockchain without stifling innovation. Some countries are embracing it with open arms, while others impose strict bans or heavy regulations.
Clarity is essential for adoption, especially in sectors like finance, healthcare, and legal services where compliance is non-negotiable.
Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
Proof of Work blockchains, like Bitcoin, consume vast amounts of electricity due to their mining processes. This has led to widespread criticism, especially in an era focused on climate change and sustainability.
Newer models like Proof of Stake (used by Ethereum 2.0) offer a greener alternative. These systems don’t require energy-intensive mining and drastically reduce the environmental footprint.
Still, the energy debate remains a hot topic and is pushing developers toward more sustainable solutions.
How to Start Learning About Blockchain
Free Resources and Online Courses
If you’re eager to get into the world of blockchain, the good news is that there’s no shortage of free, high-quality learning material available online. From YouTube tutorials to massive open online courses (MOOCs), you can build a solid foundation without spending a dime.
Start with platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy. They offer beginner-friendly courses such as “Blockchain Basics” and “Blockchain for Business.” Many of these are taught by top universities or tech companies and are designed for people without a technical background.
You can also explore tutorials on YouTube, where creators break down complex blockchain topics using visuals, analogies, and real-life examples. Want to see how smart contracts work in action? There’s a video for that. Curious about building your first decentralized app? There’s a walkthrough for that too.
Bookmark websites like theblockchainmastery.com (your own platform!) to stay updated with beginner-friendly content, guides, and insights tailored for non-techies who want to master this powerful technology.
Books and Communities
Books are another great resource. Some top recommendations include:
- Blockchain Basics by Daniel Drescher
- The Basics of Bitcoins and Blockchains by Antony Lewis
- Mastering Bitcoin by Andreas Antonopoulos
These titles cover the history, mechanics, and potential of blockchain without overwhelming readers.
Meanwhile, joining online communities can supercharge your learning. Subreddits like r/Blockchain and r/CryptoCurrency, Telegram groups, and Discord servers are buzzing with active discussions. Ask questions, share resources, or just lurk and learn—it’s all valuable.
Don’t forget about real-world meetups and conferences. These events are great for networking, learning from experts, and getting hands-on experience.
Staying Updated with Blockchain News
Blockchain evolves rapidly. New projects, technologies, and regulations pop up almost daily. To stay ahead, follow news sources like:
- CoinDesk
- The Block
- CryptoSlate
- Decrypt
Set Google Alerts for keywords like “blockchain news,” “Ethereum updates,” or “Web 3.0” to keep tabs on developments. Listening to blockchain-focused podcasts or subscribing to newsletters can also help you learn on the go.
Most importantly, make learning a habit. Blockchain is here to stay—and the more you understand, the more you’ll be able to participate in shaping its future.
Conclusion
So, there you have it—blockchain, stripped of the jargon and made for non-techies. At its core, blockchain is about creating a digital world that’s more secure, transparent, and fair. It’s a system that removes the need for middlemen, eliminates fraud, and gives power back to the people.
We’ve explored how blocks and chains work, what makes blockchain so trustworthy, and how it’s already revolutionizing industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chains. You’ve learned the truth behind common myths and seen what the future could look like with blockchain powering everything from smart contracts to a decentralized internet.
This isn’t just a trend. Blockchain is a foundational shift—like the internet was in the ‘90s. And just like then, the people who understand it first will be the ones who benefit most.
Whether you’re curious, cautious, or already convinced, now’s the perfect time to start your blockchain journey. Dive deeper, ask questions, and most of all—stay curious. The future is decentralized, and it’s already begun.
FAQs
What is the main purpose of blockchain?
Blockchain’s main purpose is to provide a secure, transparent, and decentralized method of recording transactions and data. It removes the need for intermediaries and ensures trust between parties.
Can blockchain be hacked?
While no system is 100% hack-proof, blockchain is extremely secure due to its decentralized nature and cryptographic structure. Hacking a blockchain would require altering every block on every node—a nearly impossible task.
Do I need coding skills to understand blockchain?
Nope! While coding helps if you want to develop blockchain apps, understanding the basics—how it works, why it’s secure, and how it’s used—doesn’t require any technical background.
Is blockchain the same as cryptocurrency?
Not exactly. Cryptocurrency is one application of blockchain. Blockchain is the technology behind cryptocurrencies, but it also powers things like digital identity, supply chain tracking, and secure voting systems.
What industries are most affected by blockchain?
Finance, healthcare, logistics, real estate, and even entertainment are being transformed by blockchain. Any sector that relies on trust, security, or transparency stands to benefit.
Please don’t forget to leave a review.